The Rise of Snacking: How Canadians Are Redefining Meals and Connections
The snacking industry in Canada has experienced significant growth, evolving from a simple hunger fix to a multifaceted experience that fosters connection, convenience, and cultural expression. This expansion is evident across various sectors, from restaurants to convenience stores.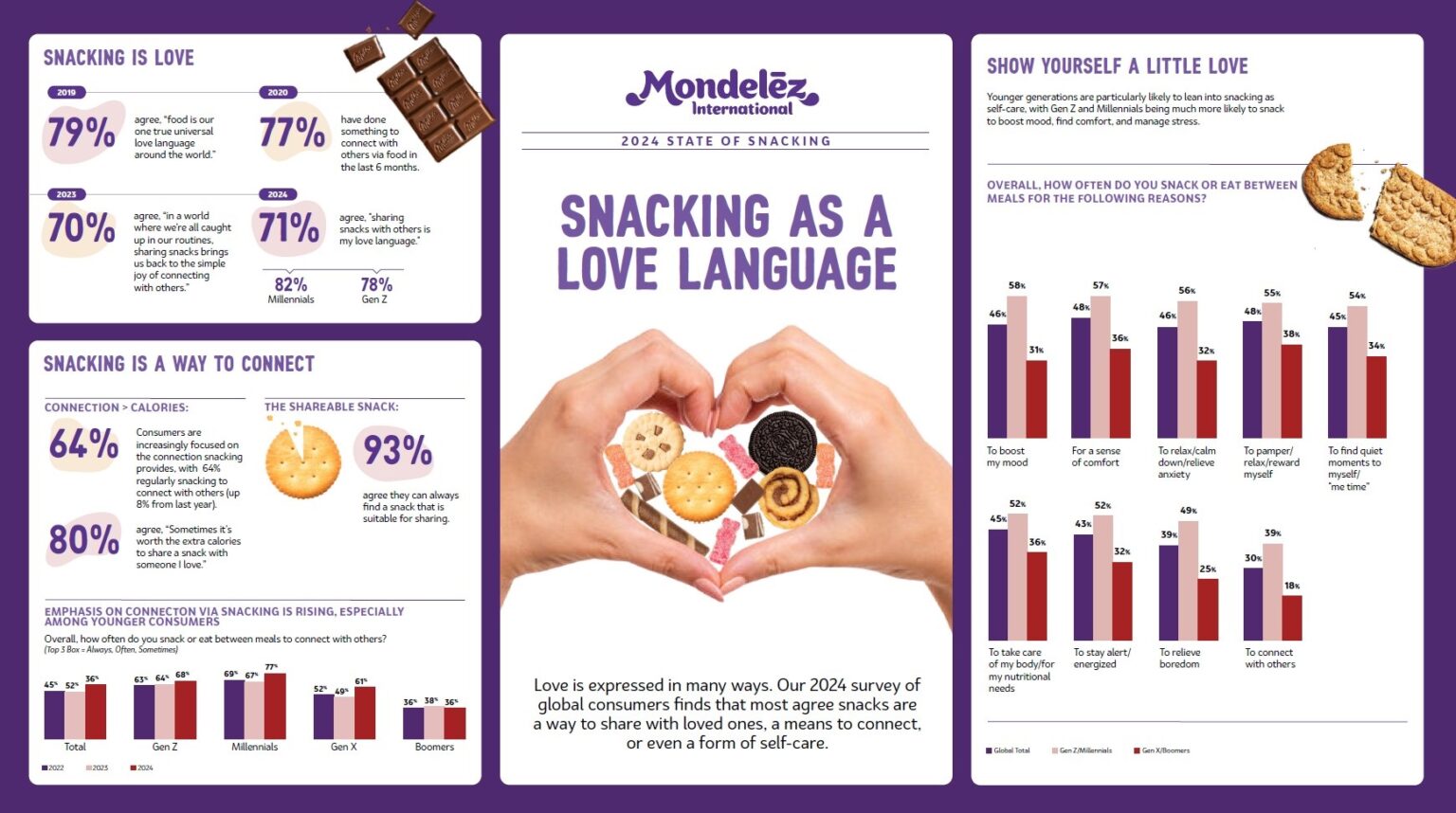
Snacking as a Social Connector
According to the sixth annual State of Snacking report by Mondelēz International, snacking has become a means for individuals to connect with loved ones. The report reveals that 71% of global consumers view sharing snacks as a “love language,” marking an 8% increase from the previous year. This sentiment is particularly strong among Millennials and Gen Z, with 64% of respondents regularly snacking to bond with others, reflecting an 8% rise from the prior year.
Shift from Traditional Meals to Snacking
The preference for snacking over traditional meals has been on the rise. Mondelēz International’s third annual State of Snacking report indicates that 64% of consumers now favor snacking or small meals over conventional mealtime structures, a 5% increase since 2019. This trend is even more pronounced among younger generations, with 75% of Gen Z replacing at least one meal daily with a snack.
Cultural Influence on Canadian Snacking
Canada’s diverse culinary landscape has significantly influenced its snacking culture. Regional specialties such as poutine, Montreal-style hot dogs, and donairs exemplify how traditional dishes have been adapted into popular snack options. These items are readily available from street vendors and convenience stores, showcasing the integration of cultural flavors into the snacking industry.
Health and Wellness Considerations
Health-conscious consumers are driving demand for snacks that align with their wellness goals. The third annual State of Snacking report highlights that mindfulness and well-being considerations are increasingly important in snacking choices. This shift has led to a broader selection of healthier snack options in both restaurants and retail outlets, catering to consumers seeking nutritious alternatives without compromising on convenience.
Conclusion
The snacking category in Canada continues to grow, reflecting changes in consumer behavior and preferences. As snacks become integral to social interactions, meal structures, cultural expression, and health considerations, the industry is poised to innovate and adapt, offering diverse options that cater to the evolving tastes and lifestyles of Canadians.

